40 Amazing Roman Colosseum Facts | 2024 (with Photos)
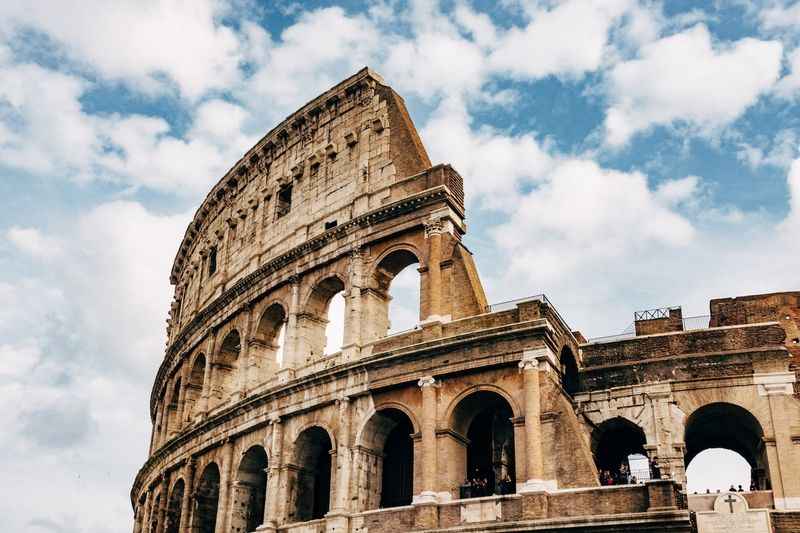

The Roman Colosseum, also called the Flavian Amphitheater, is an elliptical structure that stands as a testament to the grandeur and power of the Roman Empire.
The Colosseum is located east of the Roman Forum and Palatine Hill on Piazza del Colosseo. It is among the most popular tourist attractions in Rome, drawing millions of visitors each year.
This famous monument is among the Seven Wonders of the Modern World and is open for visitors to explore the Colosseum's history and immerse themselves in the vibrant past of the Roman people.
Let's dive into our top 40 facts about the Roman Colosseum.
Most Recommended Thing to Do
Top Choice Hotel
Hassler Roma
Our Top Choice Restaurant
Our Top Choice Bar for Nightlife
Best Time to Visit
Spring and autumn, avoiding peak summer and winter.
Average Temperature
The average temperature in Rome, Italy is mild.
Transportation Options
Buses, trams, metro, taxis, bikes, scooters, walking, car rentals.
Average Cost ($, $$, $$$)
$$
My Top Recommendation
Experience the awe-inspiring grandeur of the Roman Colosseum, an iconic symbol of ancient history. Marvel at its monumental architecture, steeped in tales of gladiatorial combat and imperial opulence. Immerse yourself in the atmosphere of the ancient amphitheater, where the echoes of a bygone era still linger.
Explore the labyrinthine corridors and imagine the roar of the crowd as warriors faced off in epic battles. Don't miss the opportunity to stand in the heart of one of the world's most renowned landmarks and witness the legacy of Rome's glorious past firsthand.
What You'll Need to Bring
- Comfortable walking shoes
- Lightweight clothing for warm weather
- Sunscreen and sunglasses
What Not to Miss
- Vatican City
- Colosseum
- Trevi Fountain
- Pantheon
- Spanish Steps
What to Avoid
- Overpriced tourist traps
- Crowded public transportation
- Pickpockets in busy areas
Table of Contents
1. It Was Formerly Called the Flavian Amphitheatre

The iconic structure we now know as the Colosseum was initially called the Flavian Amphitheatre. Named after the Flavian dynasty, specifically Emperor Vespasian and his sons, Titus and Domitian, who commissioned its construction.
This grand amphitheater featured a massive arena where gladiators battled and spectacles took place. However, the original name was eventually changed to the Colosseum.
The reason behind this change was the colossal statue of Emperor Nero, known as the Colossus of Nero, which stood at the entrance of the nearby Domus Aurea, a lavish palace built during Nero's reign.
The association with Nero led to the amphitheater being called the Colosseum, a name that has endured throughout history.
2. The Colosseum Was Associated with the Colossus of Nero
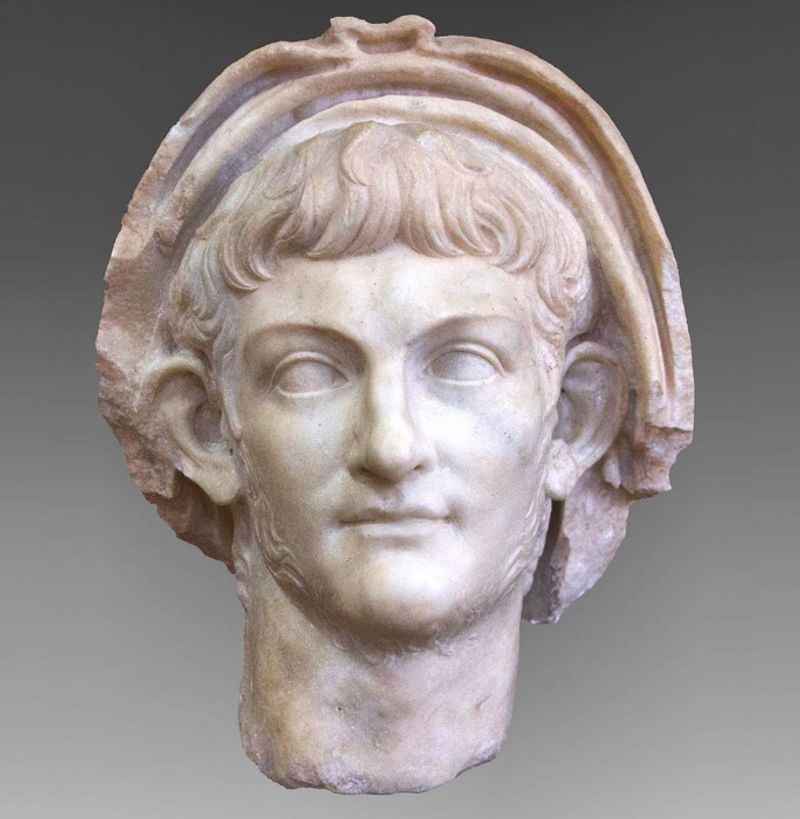

The name "Colosseum" is associated with the Colossus of Nero, a colossal statue that once stood near the amphitheater.
The Colossus of Nero was a massive bronze statue, measuring approximately 30 meters (98 feet) in height, depicting the emperor Nero himself. The statue was originally erected in the vicinity of the Domus Aurea, Nero's lavish palace.
When the Flavian dynasty took over, including Emperor Vespasian, they repurposed the land and constructed the Colosseum.
Over time, the "Colosseum" became synonymous with the grand amphitheater, named after the colossal statue that once dominated the area, despite the fact that the statue was eventually removed.
3. It Was Not Built on an Artificial Lake
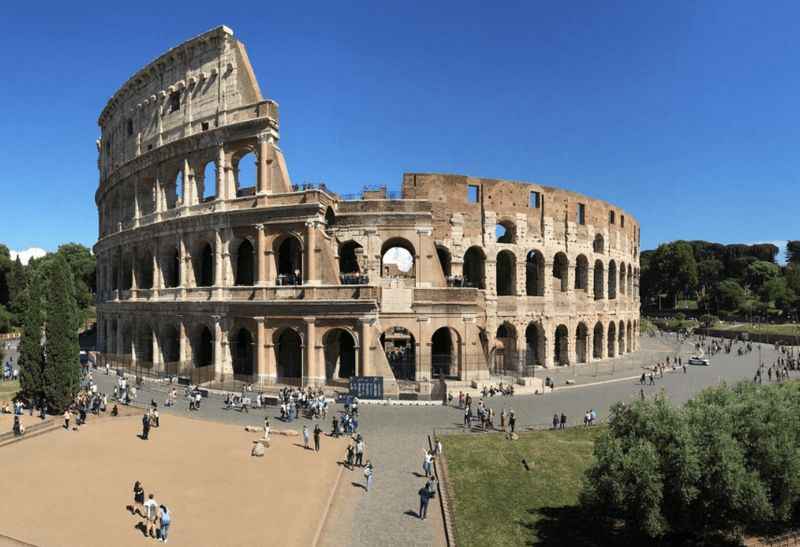

Contrary to popular belief, the Colosseum was not built on an artificial lake. The construction of this iconic amphitheater took place on flat land in Rome, and it was not surrounded by water. The Colosseum stands as a testament to the architectural brilliance of ancient Rome.
From its inception to its present day, it is regarded as one of the marvelous architectural wonders of the world, creating long lines of tourists who would like to see the monument at its entrance.
The grandeur, scale, and design of the Colosseum continue to captivate visitors, who marvel at its impressive architecture and the historical significance it represents.
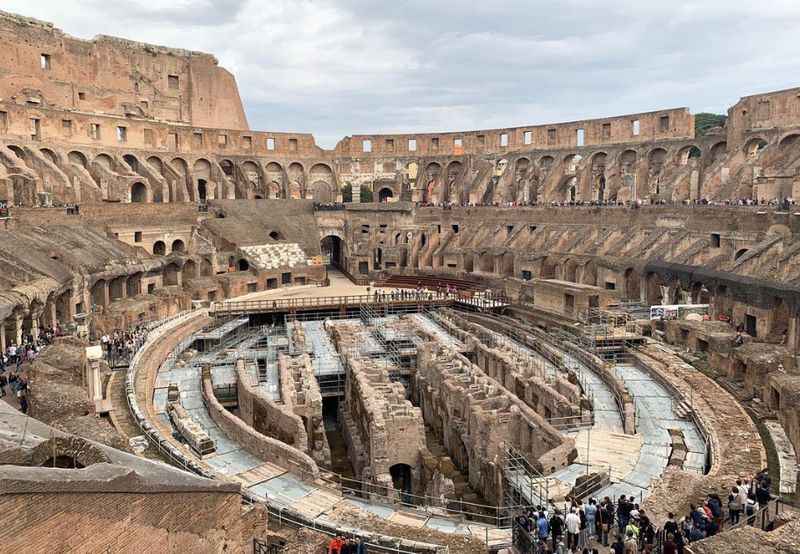
4. It Has an Underground Tunnel System
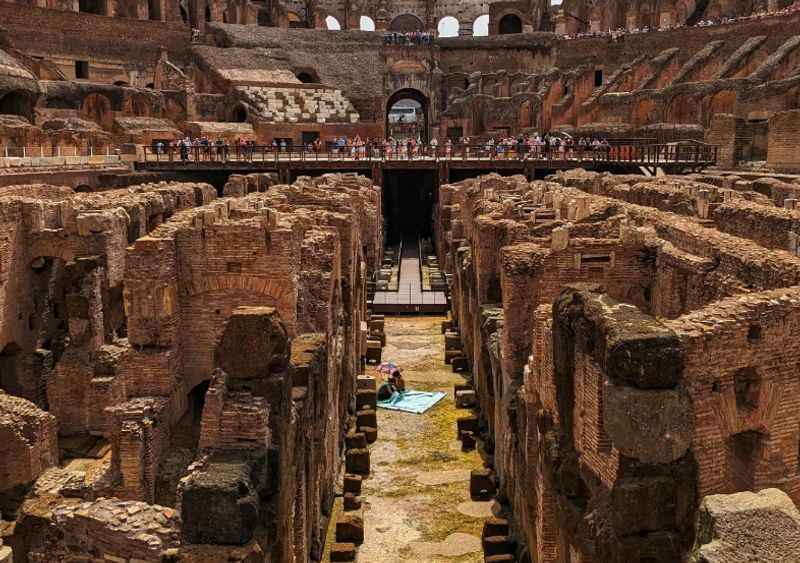

Beneath the impressive arena floor of the Colosseum lies a complex system of underground tunnels known as the hypogeum.
These tunnels were a vital part of the Colosseum's operations, serving as storage areas for equipment, holding pens for animals, and living quarters for gladiators.
Trap doors were used to bring animals, such as lions, into the arena from below for thrilling animal hunts.
Rediscovered in the 19th century, the hypogeum offers visitors a unique perspective, allowing them to step foot into the shoes of the gladiators and see the Colosseum from their vantage point.
However, access to the hypogeum, along with the Arena and Gate of Death, requires special access tickets, which provide an opportunity to explore off-limit areas like the top levels and hypogeum.
The basic ticket will not give you access to these areas.
5. The Colosseum Was Made from Travertine Stone
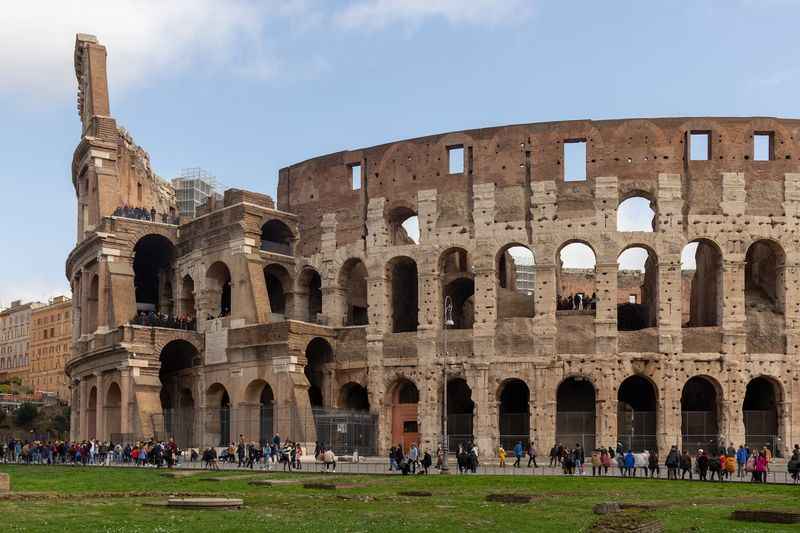

Travertine stone played a significant role in the building of the Roman Colosseum, also known as the Flavian Amphitheater.
When the construction of the Colosseum commenced under Emperor Vespasian in 72 AD, travertine was chosen as the primary building material. Quarried from nearby Tivoli, travertine limestone provided the structure with durability and a distinct aesthetic.
Originally, the Roman Colosseum was adorned with marble, but over time, much of it was removed and repurposed for other buildings in Rome. Interestingly, remnants of the marble can still be found on the upper portions of the Colosseum today.
This magnificent amphitheater stood witness to thrilling gladiator battles and continues to be a testament to the grandeur of ancient Rome.
6. It is A Symbol of Christianity
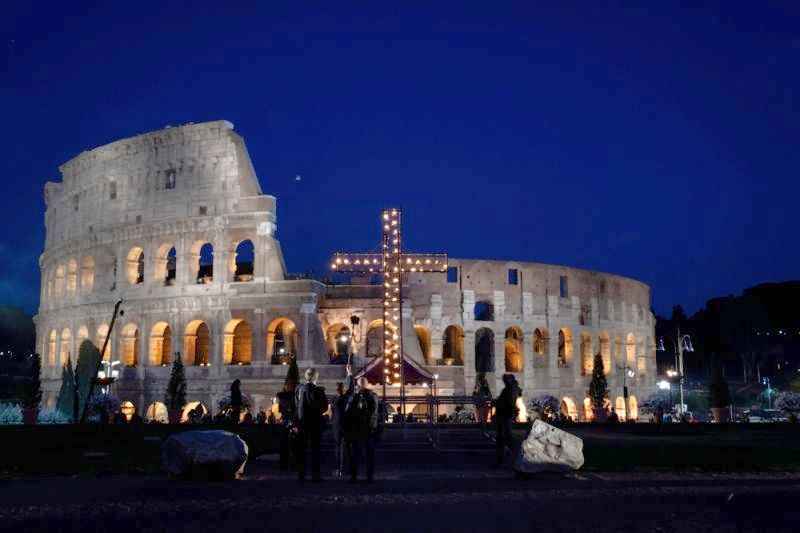

The Colosseum, located in Rome, Italy, holds profound significance as a symbol of Christianity. The association stems from its historical connection to early Christian martyrs who suffered persecution within its walls.
To honor their memory, every Good Friday the Pope leads the Way of the Cross procession in the Colosseum. During this solemn ceremony, the stations of the Cross are reenacted, reflecting on the suffering and sacrifice of Jesus Christ.
This annual Good Friday event serves as a powerful reminder of the enduring faith of early Christians and the resilience of Christianity itself.
The Colosseum stands as a poignant symbol, uniting history, faith, and the enduring spirit of Christianity.
7. The Grand Opening Was Brutal
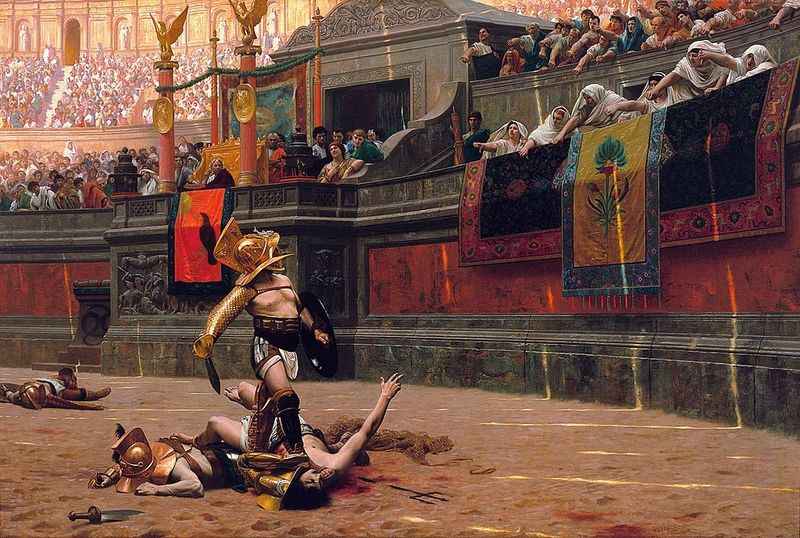

You may be wondering, when did the Colosseum open? When the Colosseum was inaugurated by Emperor Titus in 80 AD, it marked a grand opening with 100 days of games known as the inaugural games.
These festivities included gladiatorial battles, wild animal hunts, and elaborate spectacles that captivated the spectators. Unfortunately, thousands of gladiators met their demise in the blood-soaked arena during these inaugural games.
The Colosseum's grand opening was a momentous occasion filled with celebration and entertainment, showcasing the might and glory of the Roman Empire.
However, as time went on, the Colosseum's purpose shifted, and public fights ceased in the 6th century, bringing an end to the era of gladiatorial combat within its hallowed walls.
8. There Were Other Uses of the Colosseum
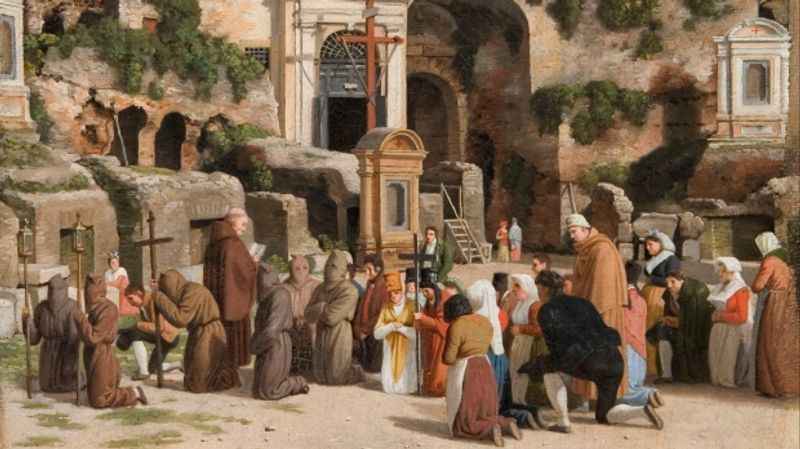
The Colosseum served purposes beyond fights between gladiators for entertainment. As public opinion shifted in the 6th century AD, the perception of public spectacles changed.
The Colosseum was adapted to suit different needs, including being used as a church and a storehouse. It underwent transformations to accommodate these new functions while preserving its architectural grandeur.
The conversion of the Colosseum into a church allowed it to be repurposed as a place of worship, offering a different form of spiritual experience within its historic walls.
This multifaceted utilization of the Colosseum demonstrates its adaptive nature and its ability to reflect the evolving cultural, social, and religious dynamics of ancient Rome.
9. It Was Used for Reenactments of Naval Battles
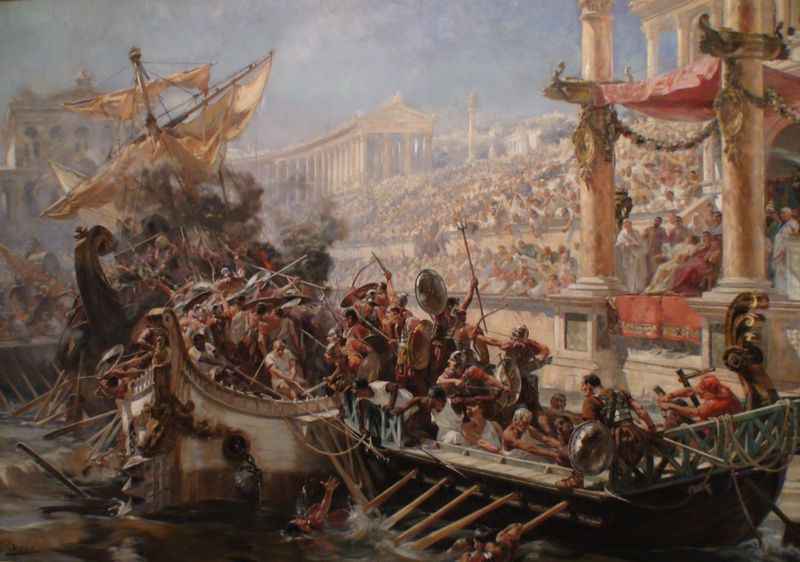

The Colosseum, known for its gladiatorial contests, also saw reenactments of naval battles during its time.
On the order of Emperor Titus, the amphitheater was transformed into a water-filled stage, where historic sea battles between Athens and Syracuse were recreated.
This awe-inspiring spectacle showcased the engineering ingenuity of the Romans, as they recreated naval warfare within the confines of the Colosseum.
The inclusion of water, ships, and skilled performers made these reenactments a breathtaking sight for the spectators.
This unique usage of the Colosseum highlighted the versatility and grandeur of the amphitheater as it transported the audience back in time to witness epic battles from history.
10. The Colosseum Suffered Many Natural Disasters
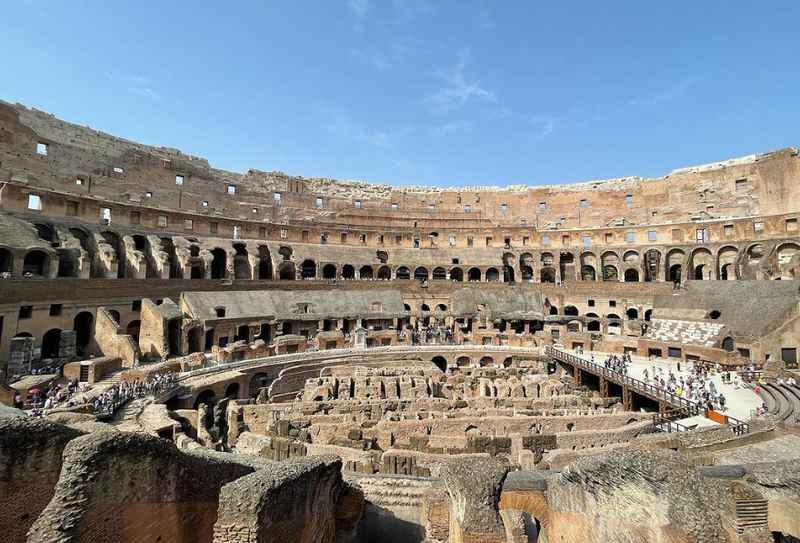

Throughout its long history, the Colosseum faced destruction on several occasions due to natural disasters.
Earthquakes were among the most devastating, causing severe damage to the iconic structure.
Over time, the Colosseum suffered from neglect and pillaging, further contributing to its deterioration.
However, restoration efforts began in the 19th century to preserve and revive this remarkable ancient monument.
The extensive restoration work aimed to repair and reconstruct parts of the Colosseum, ensuring its survival for future generations to appreciate.
Today, visitors can witness the grandeur of the Colosseum, standing as a testament to both the resilience of ancient Roman engineering and the commitment to preserving cultural heritage.
11. The Colosseum is Several Stories High
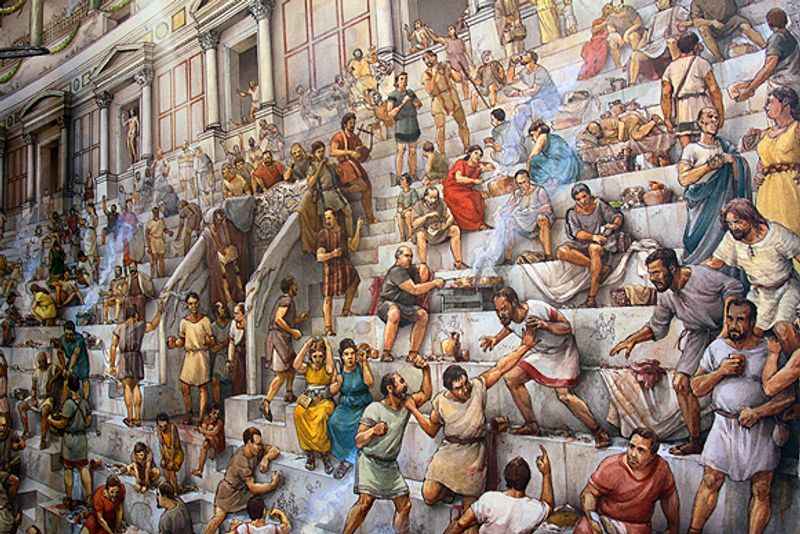

The Colosseum, in present-day Rome, stands as one of the most iconic tourist attractions in the world. This colossal amphitheater impresses visitors with its immense size, standing several stories high.
Its elliptical shape, with a circumference of approximately 527 meters, encompasses multiple levels that once accommodated seating for thousands of spectators.
While the upper levels have suffered significant damage over the centuries, the sheer magnitude of the Colosseum's original design is still evident.
Its towering presence serves as a tangible reminder of the architectural prowess of ancient Rome and continues to awe and inspire visitors from around the globe.
12. The Colosseum Has a Large Seating Capacity
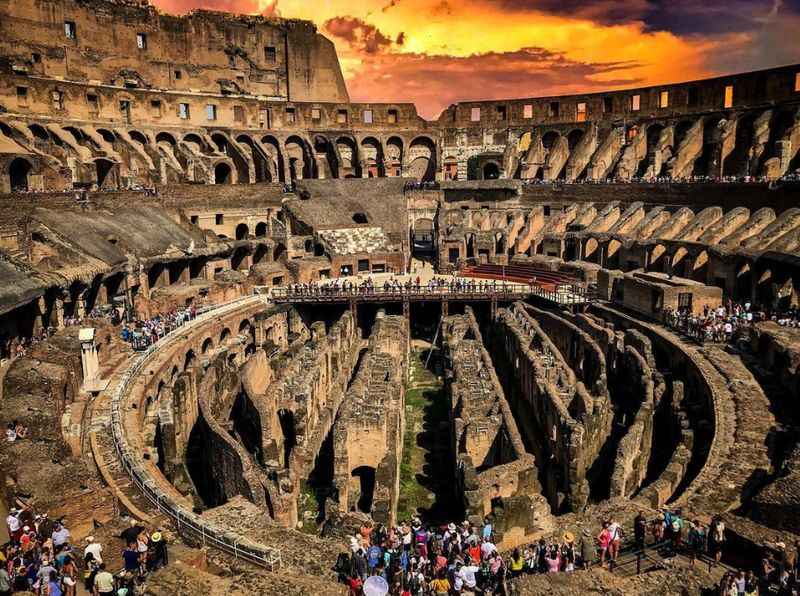

The Colosseum, renowned for its grandeur and historical significance, boasted an impressive seating capacity in its prime.
The amphitheater was designed to accommodate a vast number of spectators, providing seating for an estimated 50,000 to 80,000 people.
The seating arrangement was carefully organized to ensure optimal visibility and comfort for the audience. The lower tiers, reserved for the elite and dignitaries, offered the best views of the gladiatorial contests and other spectacles.
As one ascended to the higher levels, seating was available for the general public.
The massive seating capacity of the Colosseum reflects the immense popularity and significance of the events held within its walls.
13. The Colosseum Was Built in 8 Years

The construction of the Colosseum stands as a testament to the remarkable efficiency and engineering prowess of ancient Rome.
Considering the immense size and complexity of the structure, the speed at which it was built is truly astonishing.
Work commenced under Emperor Vespasian in72 AD and was completed in 80 AD, an impressive feat accomplished in just eight years.
The efficient methods employed, including the use of travertine stone and a well-organized workforce, contributed to rapid progress.
This allowed the Colosseum to become a magnificent centerpiece of Roman architecture and an enduring symbol of Roman engineering excellence.
14. It Has a Huge Architectural Influence
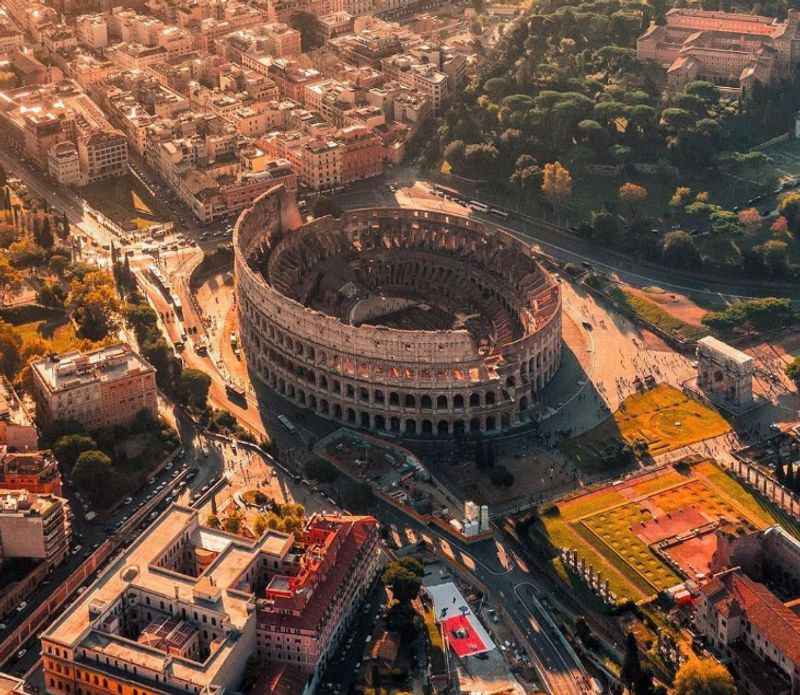

The architectural influence of the Colosseum extends far beyond its immediate surroundings. This magnificent amphitheater, with its innovative design and engineering, has had a profound impact on the development of architectural principles.
Its iconic elliptical shape, tiered seating, and advanced systems for crowd control and access have served as inspiration for numerous structures throughout history.
The Colosseum's grandeur and scale have influenced the design of stadiums, arenas, and amphitheaters around the world.
Its enduring legacy as a symbol of architectural brilliance continues to inspire architects and designers, showcasing the timeless beauty and functionality of Roman architecture.
15. The Colosseum Has Impressive Dimensions
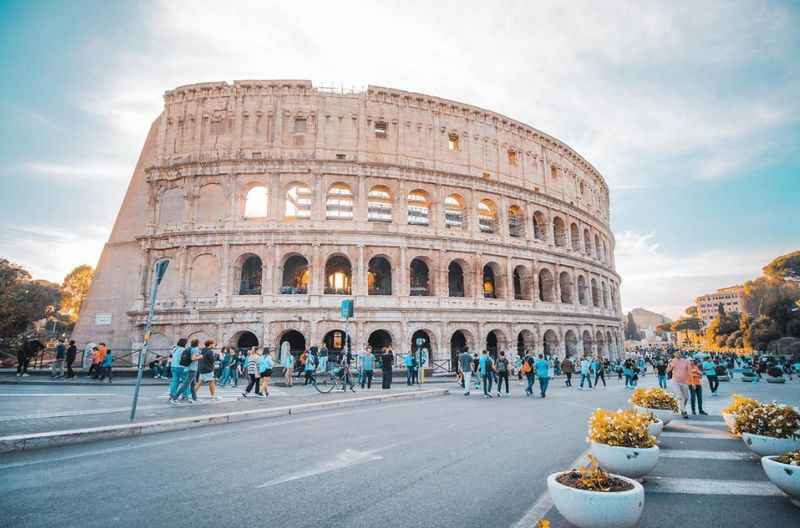

The Colosseum's colossal dimensions are a testament to the grandeur of ancient Roman architecture. This awe-inspiring structure stands as an imposing symbol of Roman power and engineering prowess.
The amphitheater spans approximately 189 meters in length, 156 meters in width, and originally stood at a height of over 48 meters tall.
Its shape, composed of limestone and concrete, accentuates its massive scale. The Colosseum's vast interior once housed seating for tens of thousands of spectators, accommodating various events and spectacles.
The sheer size and proportions of the Colosseum continue to captivate visitors, serving as a tangible reminder of the architectural magnificence of ancient Rome.
16. It Had a Retractable Roof
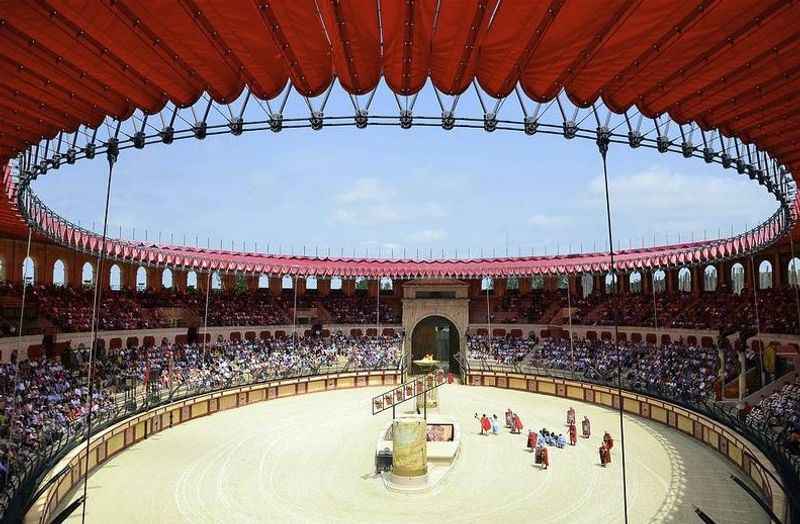

The Colosseum, a marvel of ancient Roman engineering, boasted an innovative feature that resembled a retractable roof.
Known as the velarium, this canvas awning was suspended above the seating area, providing shade and protection from the elements. Consisting of a vast network of ropes, pulleys, and masts, the velarium could be extended or retracted as needed.
This ingenious mechanism allowed the audience to enjoy events in comfort, shielding them from the scorching sun or offering respite during rainfall.
The retractable roof of the Colosseum exemplifies the advanced engineering techniques employed by the Romans and their commitment to creating an exceptional experience for spectators in this monumental structure.
17. The Colosseum Boasted Public Restrooms

Public restrooms were an essential feature of the Colosseum, catering to the needs of the large crowds who gathered to witness the spectacles within its walls. The ancient Romans placed great importance on sanitation and hygiene, and the Colosseum was no exception.
The amphitheater was equipped with numerous public restrooms strategically located throughout the complex, offering convenience and comfort to both spectators and participants. These restrooms featured a system of running water, drainage, and communal seating arrangements.
The provision of public restrooms at the Colosseum demonstrated the Romans' remarkable attention to public welfare and their commitment to ensuring a pleasant and hygienic experience for all who visited the renowned venue.
18. It Also Had Decorative Statues
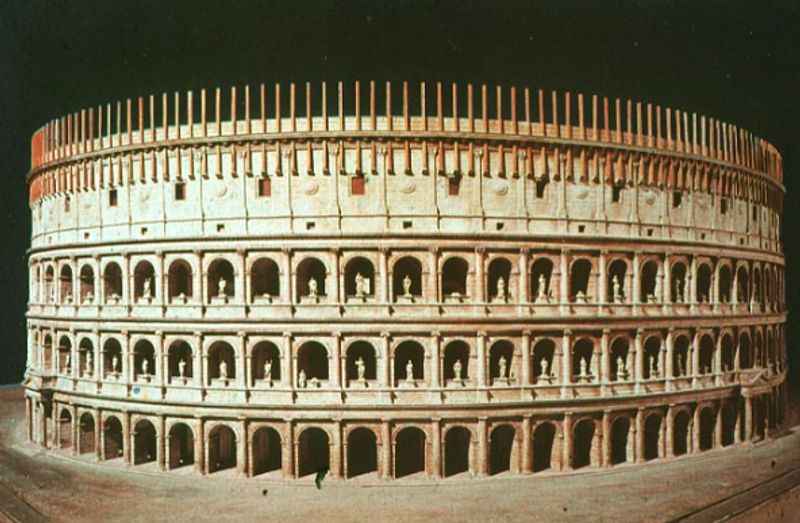

Decorative statues adorned the Colosseum, adding to its majestic allure. The exterior of this iconic building was once adorned with a multitude of statues, ranging from gods and goddesses to mythological figures and historical heroes.
These intricately crafted statues, made from various materials including marble and bronze, were strategically placed along the arches and cornices, showcasing the artistic mastery of ancient Roman sculptors.
While most of these statues have been lost to time, some remnants and replicas can still be seen today. The inclusion of decorative statues further emphasized the grandeur and cultural significance of the Colosseum, making it a visually stunning architectural masterpiece.
19. The Colosseum Suffered Stone Pillaging
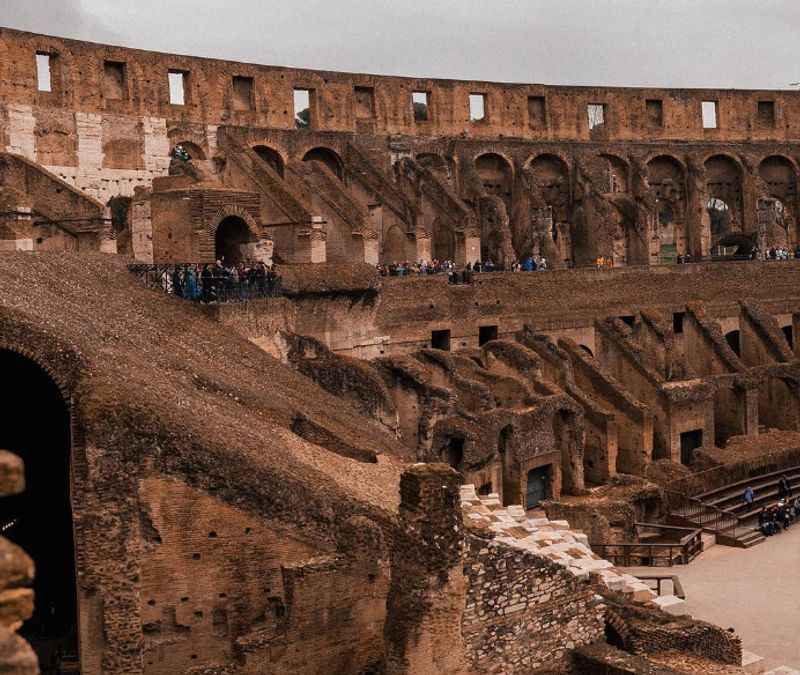

The Colosseum endured years of stone pillage, where its precious materials were looted for various purposes.
Over time, the demand for construction materials led to extensive quarrying of the Colosseum's travertine stone. Additionally, several destructive events, including earthquakes and fires, caused further damage to the structure.
As a result, much of the original marble cladding and decorative elements were removed from the Colosseum and repurposed for other buildings. Despite this pillaging, traces of the Colosseum's former glory can still be observed, with remnants of marble visible on the top levels of the building.
The stone pillage stands as a testament to both the enduring allure of the Colosseum and the value placed on its remarkable architectural materials.
20. It Had Various Medieval Transformations
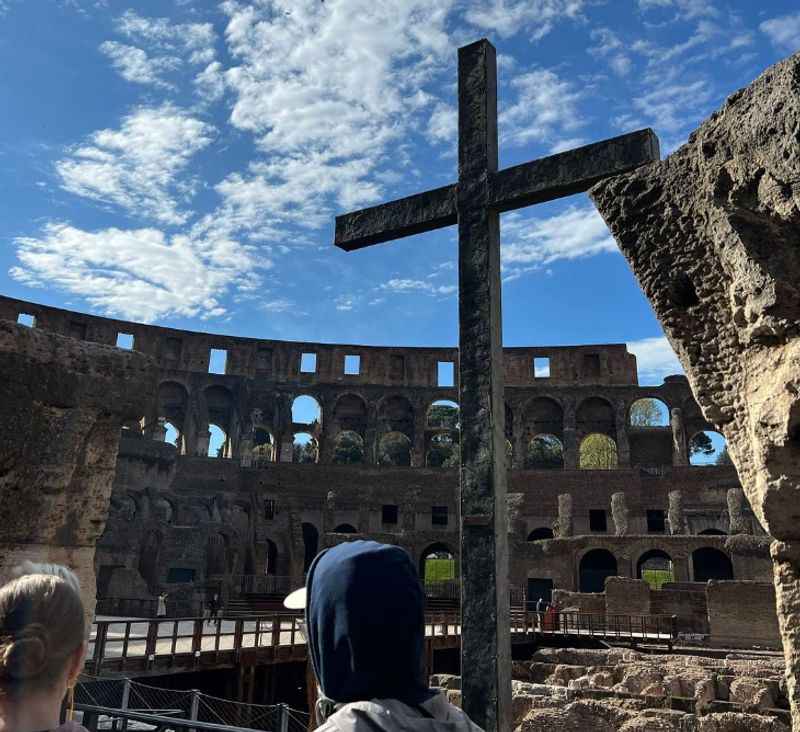

During the Middle Ages, the Colosseum underwent significant transformations that shaped its appearance and purpose. The once-grand Colosseum became a fortress, with the inclusion of fortified walls and towers for defensive purposes.
The strategic location of the Colosseum atop the Esquiline Hill made it an ideal defensive stronghold. Additionally, during this period, the interior of the Colosseum was repurposed for various activities, such as workshops, housing, and even as a place for religious worship.
These medieval transformations showcased the adaptability and resilience of the Colosseum, as it continued to serve the evolving needs of the society it stood within.
21. It Was a Site of Papal Consecration
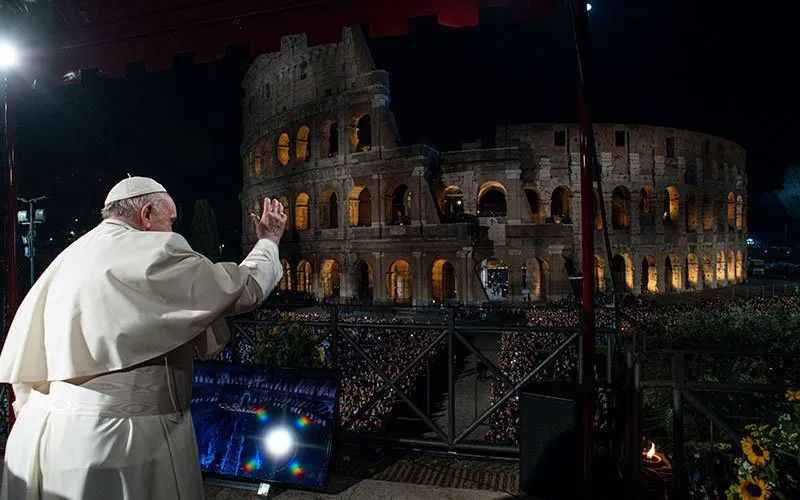

The Colosseum holds deep significance in the history of the papacy, as it became a site of papal consecration during the medieval period.
In a solemn ceremony, newly elected popes were traditionally crowned at the Colosseum, symbolizing their authority and spiritual leadership. This practice started in the 14th century and continued for several years.
The Colosseum's grandeur and historical significance provided a fitting backdrop for these momentous events, capturing the attention of both the clergy and the public.
The papal consecrations at the Colosseum represent the intersection of religious and historical significance, further solidifying its status as a cherished symbol of Rome and Christianity.
22. It Is an Enduring Symbol of Roman Civilization
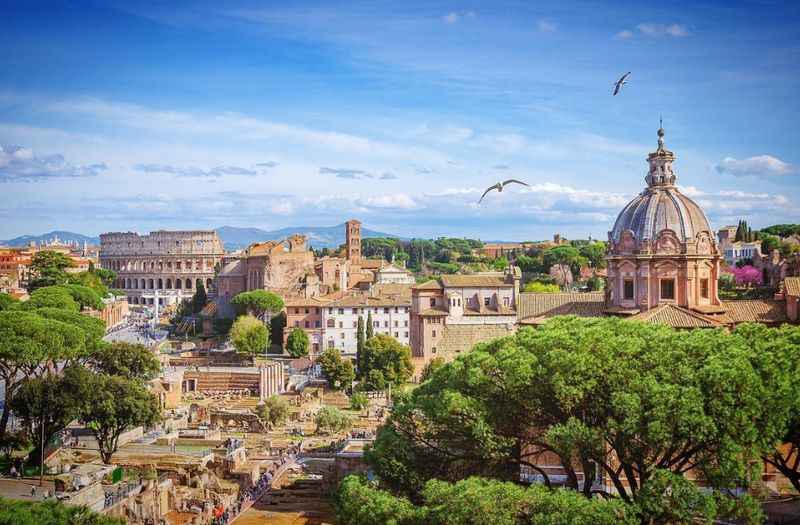

The Colosseum stands as an enduring symbol of ancient Roman civilization and architectural ingenuity. For over two millennia, this monumental structure has captivated the imaginations of people worldwide.
Its iconic silhouette, colossal dimensions, and rich historical legacy have made it an enduring emblem of Rome's grandeur and cultural heritage. The Colosseum's architectural brilliance, innovative design, and engineering feats continue to inspire awe and admiration.
It serves as a living testament to the ancient past, drawing millions of visitors each year who seek to witness its majestic presence and immerse themselves in the fascinating history it represents.
The Colosseum remains an unwavering symbol of human achievement, captivating generations and transcending time.
23. It’s Also a UNESCO World Heritage Site
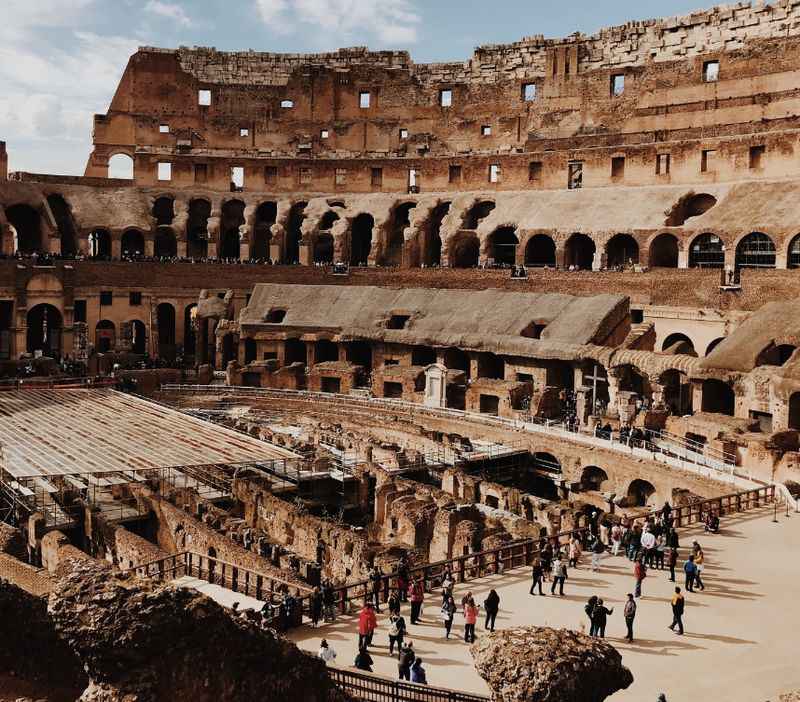

The Colosseum holds the esteemed status of being a UNESCO World Heritage Site, recognized for its outstanding universal value.
As one of the most iconic and well-preserved ancient structures, the Colosseum's inclusion on this prestigious list highlights its significance and contribution to humanity's cultural heritage.
The designation as a World Heritage Site signifies the responsibility to safeguard and preserve this architectural masterpiece for future generations.
It also emphasizes the Colosseum's universal importance, serving as a symbol of ancient Roman civilization and inspiring awe and fascination in people from all corners of the globe.
The recognition as a UNESCO World Heritage Site ensures that the Colosseum's historical legacy remains protected and celebrated on a global scale.
24. The Colosseum Features in Movies
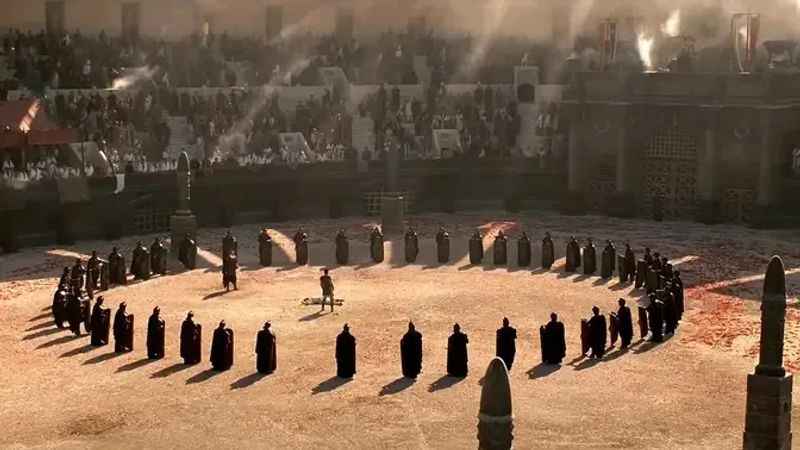

The Colosseum has not only captured the hearts of history enthusiasts but has also made a significant impact on cinema, becoming a revered "movie star" in its own right.
Its awe-inspiring architecture and timeless allure have made it a sought-after filming location for numerous movies over the years.
From epic historical dramas to action-packed adventures, the Colosseum has provided a captivating backdrop for storytelling on the silver screen.
Its iconic presence has lent an air of authenticity and grandeur to films, transporting audiences back in time and adding a touch of majesty to the cinematic experience.
The Colosseum's on-screen appearances have further solidified its status as a cultural icon, ensuring its legacy reaches beyond the realm of history books.
25. It Also Boasts Nighttime Illumination
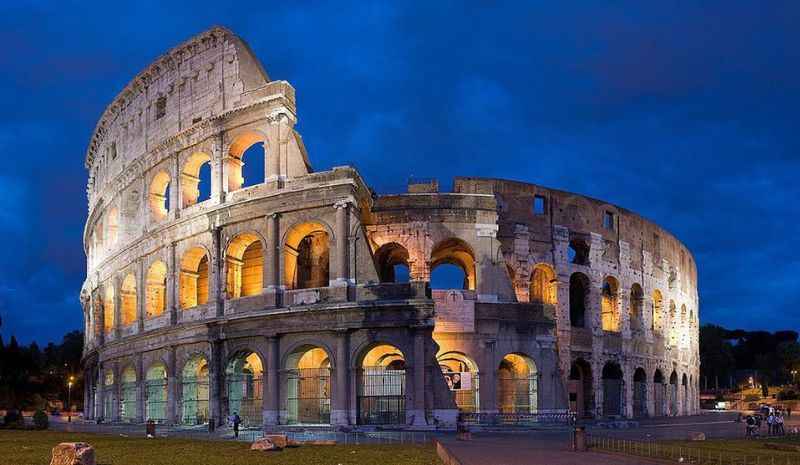

The Colosseum undergoes a breathtaking transformation when the sun sets, as it is beautifully illuminated during nighttime.
Special lighting installations have been employed to showcase the architectural grandeur of this iconic structure after dark.
The carefully designed illumination accentuates the intricate details of the Colosseum's arches, columns, and façade, casting a mesmerizing glow across its ancient stones.
The nighttime illumination not only enhances the visual appeal but also creates a magical ambiance, allowing visitors to experience the Colosseum in a different light.
This captivating display further adds to the allure and mystique of the Colosseum, offering a unique and enchanting perspective of this architectural masterpiece.
26. Historical Documentation Helps Us Understand the Colosseum

Historical documentation plays a crucial role in our understanding of the Colosseum's rich past. Through ancient writings, inscriptions, and archaeological discoveries, scholars have pieced together a comprehensive narrative of its structure, purpose, and historical significance.
The accounts of ancient historians, such as Tacitus and Suetonius, provide valuable insights into the Colosseum's inaugural games, gladiatorial spectacles, and public events.
Additionally, inscriptions found on the Colosseum itself offer glimpses into its dedication and restoration efforts.
Excavations and archaeological studies have unearthed artifacts that shed light on the daily lives of the people involved with the Colosseum, including gladiators, spectators, and workers.
The meticulous documentation of the Colosseum's history allows us to unravel the layers of its past and appreciate its enduring legacy.
27. It Has Had a Tremendous Economic Impact
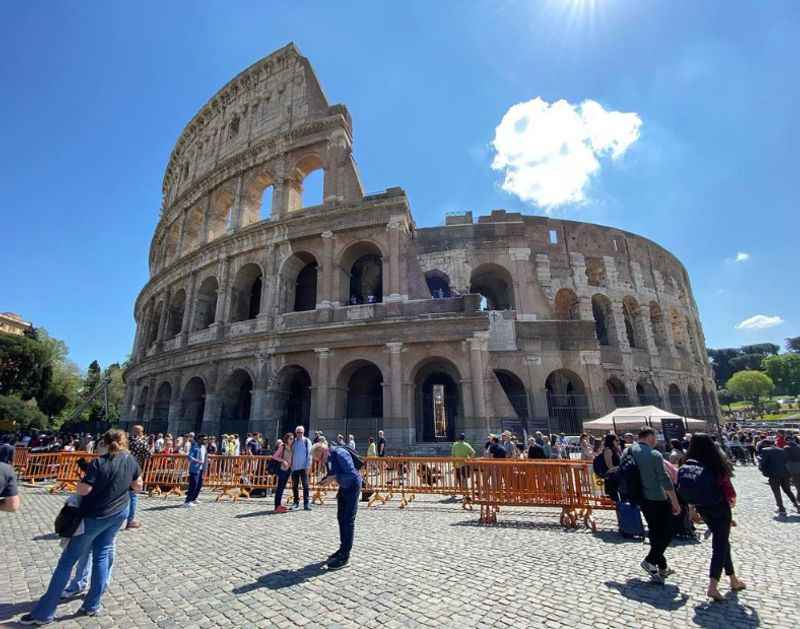

The Colosseum holds a significant economic impact, both in the past and in the present day. During ancient times, the building and operation of the Colosseum provided employment opportunities for a vast number of workers, including architects, engineers, laborers, and craftsmen.
The hosting of grand spectacles attracted thousands of visitors, contributing to the growth of local businesses and stimulating economic activity in Rome.
Today, the Colosseum continues to be a major tourist attraction, drawing millions of visitors each year. The influx of tourists supports the local economy, creating jobs in the hospitality, tourism, and retail sectors.
The Colosseum's cultural and historical significance, coupled with its status as a Heritage Site, ensures its enduring economic impact on the city of Rome.
28. Gladiatorial Training Was Rigorous
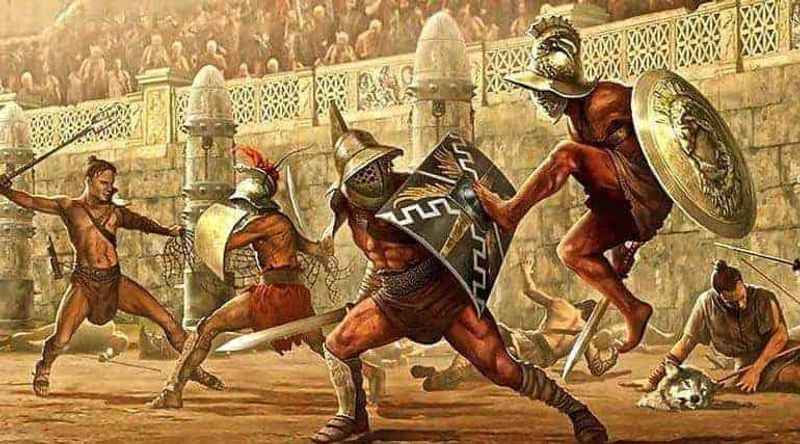

Gladiatorial training was a rigorous and disciplined process that prepared individuals for the brutal and deadly spectacles held at the Colosseum.
Gladiators underwent intense physical conditioning, combat training, and weapon mastery to hone their skills for the arena.
They trained in specialized gladiatorial schools, known as ludi, where they learned various fighting techniques and strategies.
Training sessions involved sparring with fellow gladiators, practicing with weapons, and developing agility, strength, and endurance. Trainers, known as lanistae, oversaw their progress, ensuring they were ready for the demanding battles ahead.
Gladiatorial training was not only about physical preparation but also encompassed mental fortitude, as gladiators had to face the constant risk of injury or death in their quest for glory and survival in the grand arena.
29. There Were Varying Combat Techniques
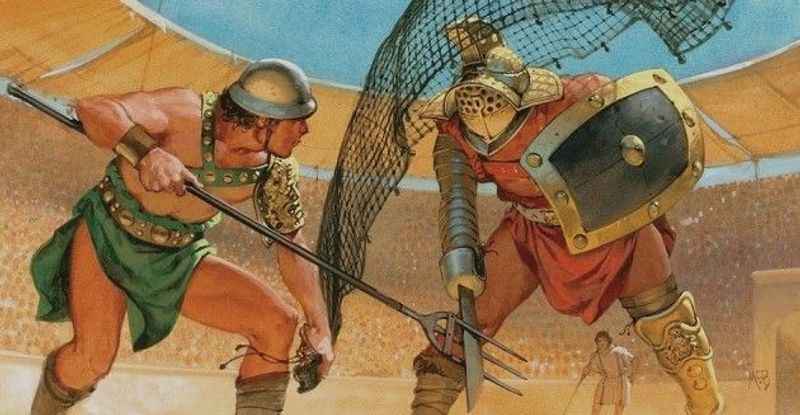

Gladiators or fighters in the Colosseum employed a range of combat techniques to entertain the crowds and increase their chances of survival. Each type of gladiator had their own specialized combat style, reflecting their specific training and equipment.
For example, the retiarius, armed with a trident and net, relied on agility and quick movements to ensnare and defeat their opponents. Secutors, on the other hand, equipped with a sword and a large shield, focused on close combat and defense.
Other techniques included parrying, thrusting, slashing, and evasive maneuvers. These fighters were skilled in reading their opponents' movements and exploiting weaknesses, employing a combination of offensive and defensive tactics to gain the upper hand in the arena.
30. It is a Symbol of Engineering Prowess
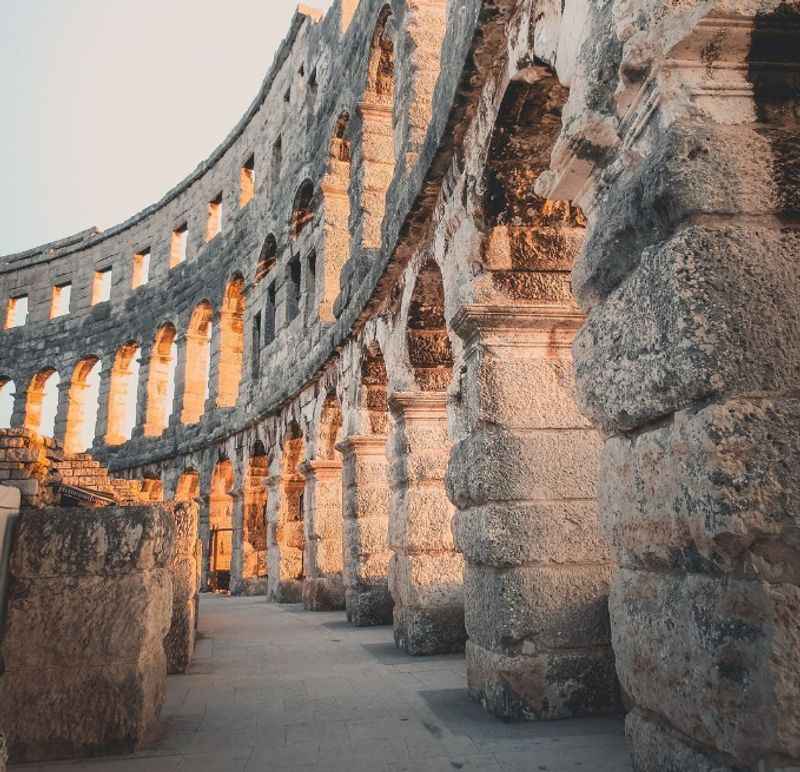

The Colosseum stands as a remarkable symbol of engineering prowess, showcasing the ingenuity and technical skill of the ancient Romans. Its innovative architectural design and building techniques were groundbreaking for its time.
The Colosseum's massive stone structure, consisting of arches, vaults, and columns, was meticulously engineered to withstand immense weight and provide optimal stability.
The intricate system of ramps, staircases, and seating arrangements allowed for efficient crowd movement and ensured clear sightlines to the arena.
The mastery of materials, such as concrete and travertine stone, contributed to the longevity and endurance of the structure.
The Colosseum's engineering marvel remains a testament to the advanced capabilities of ancient Roman builders and continues to inspire admiration and awe to this day.
31. The Colosseum Was Built to Reflect Social Hierarchy
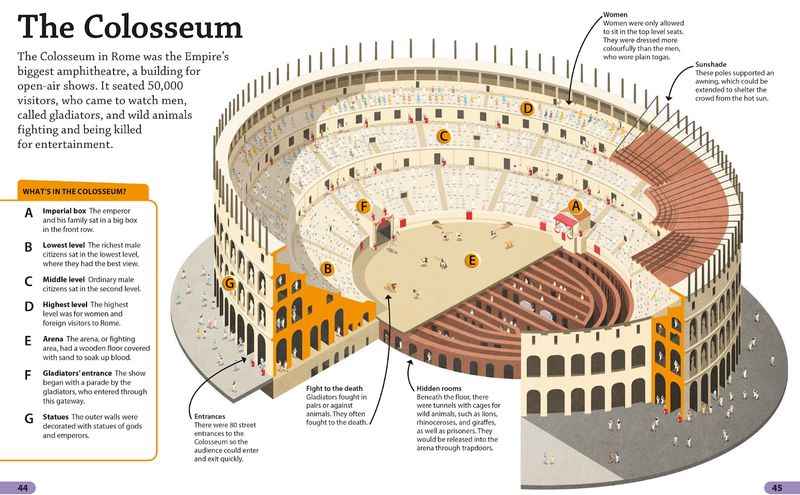
The Colosseum reflected and reinforced the social hierarchy of ancient Rome.
The seating arrangement within the amphitheater was a clear reflection of this hierarchy, with the elite occupying the prime spots closer to the arena, while the lower classes and non-citizens were seated in the upper tiers.
This division emphasized the societal divisions and the stark contrast between the privileged and the less fortunate.
The Colosseum's spectacles served as a means for the ruling class to assert their power and maintain control over the masses, providing a spectacle that both entertained and reaffirmed the social order.
The social hierarchy was further reinforced through gladiatorial fights, where the lives of enslaved fighters were controlled and manipulated by the whims of the elite.
32. It is a Testament to the Rich Heritage of Rome
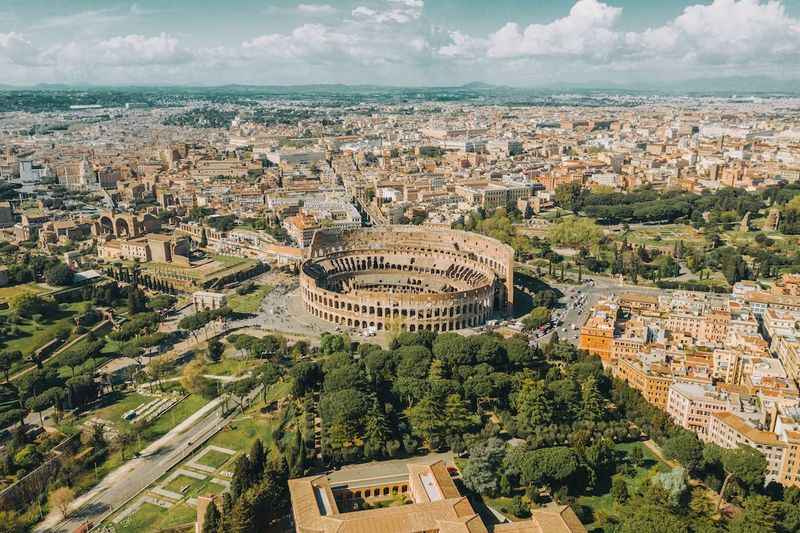

The Colosseum stands as a proud testament to the rich heritage of Rome. It embodies the grandeur and architectural brilliance of ancient Rome, showcasing the city's cultural and historical significance.
As an iconic symbol of Roman engineering and innovation, the Colosseum represents the empire's vast power and influence.
It serves as a tangible reminder of Rome's achievements in art, engineering, and governance, captivating visitors with its colossal dimensions and intricate design.
The Colosseum is a cultural treasure that allows us to connect with and appreciate the remarkable heritage of Rome.
33. It Had an Innovative Entrance System
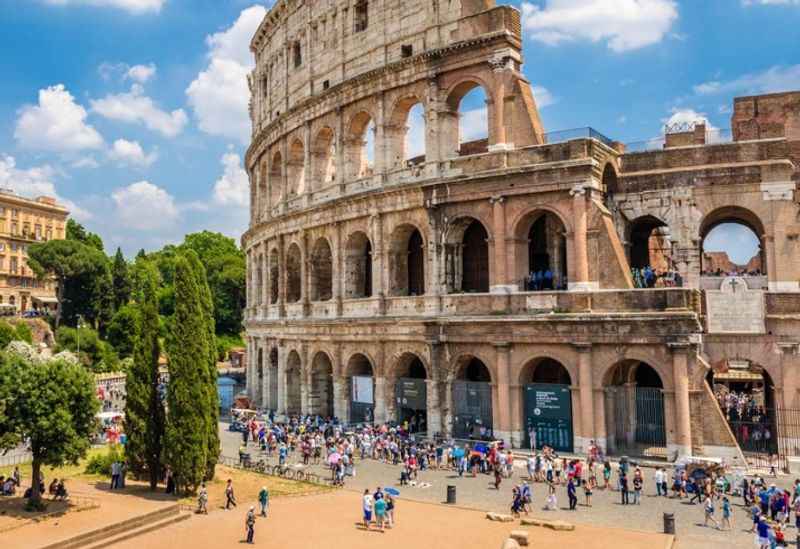

The Colosseum featured an innovative entrance system that efficiently accommodated the massive crowds attending its spectacles. It had a network of entrances, exits, and corridors strategically designed to facilitate the smooth flow of people in and out of the building.
The multiple entrances allowed for efficient crowd dispersal and reduced congestion, ensuring a seamless entry and exit experience for spectators. The use of numbered tickets and assigned seating sections further streamlined the process.
This innovative entrance system was a testament to the Romans' advanced understanding of crowd management and their ability to organize large-scale events. It contributed to the overall success and smooth operation of the Colosseum's grand spectacles.
34. It Had a Marble Facade
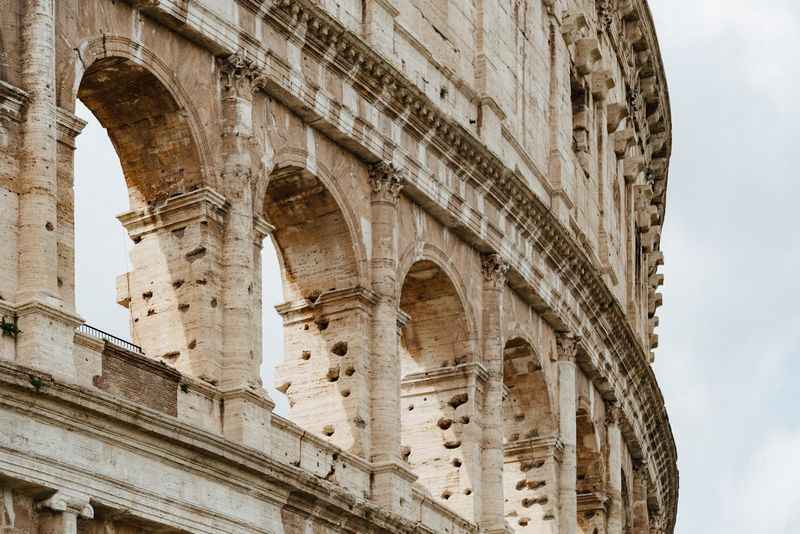

A marble facade once adorned the Colosseum’s exterior, adding to its grandeur and magnificence. The outer wall was covered in travertine stone, which was then adorned with exquisite marble cladding.
The marble facade featured a variety of colors, including white, pink, and gray, creating a visually stunning effect. However, over time, much of the marble was pillaged and repurposed for other buildings, leaving behind the exposed travertine stone that we see today.
Despite the absence of its original marble cladding, the enduring beauty of the Colosseum's facade continues to captivate visitors, serving as a tangible reminder of its ancient splendor.
35. Its Structure Reflects Architectural Order
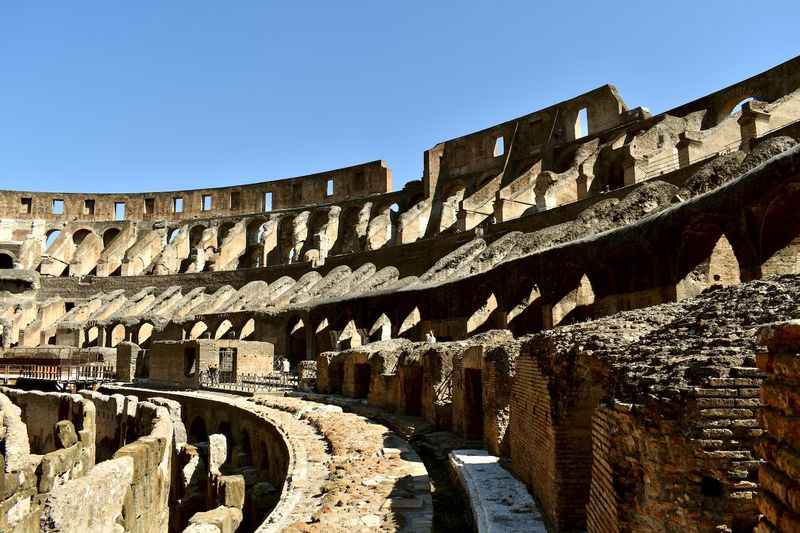

The Colosseum stands as a magnificent example of architectural order, showcasing the classical principles of Roman design.
The entire structure is built using three architectural orders: Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian.
The ground floor of the Colosseum features the robust and simple Doric order, followed by the more delicate and refined Ionic order on the second level. Finally, the topmost level exhibits the ornate Corinthian order.
This deliberate arrangement of architectural elements creates a sense of harmony and balance, elevating the Colosseum's aesthetic appeal.
The adherence to these classical orders reflects the meticulous planning and attention to detail that contributed to the enduring allure of this ancient wonder.
36. The Colosseum Has a Natural Sound Acoustic
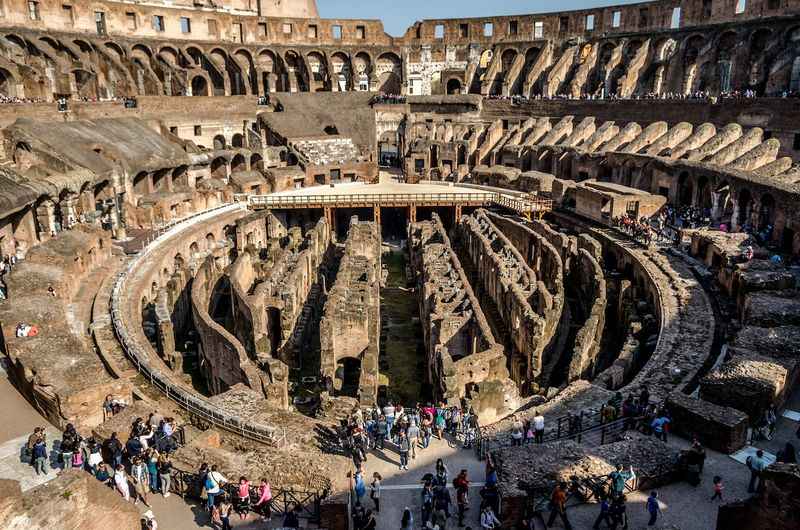

The Colosseum's architectural design incorporated natural sound acoustics, ensuring that the grand spectacles held within its walls could be heard clearly by the vast audience.
Its elliptical shape, combined with the use of arches, vaults, and inclined seating, helped to amplify sound waves and distribute them evenly throughout the space.
This clever design feature allowed even the faintest of sounds, such as the clash of weapons or the cheers of the crowd, to reverberate and resonate throughout the arena, creating an immersive auditory experience for the spectators.
The Colosseum's natural sound acoustics added to the overall spectacle, enhancing the excitement and intensity of the events taking place within its hallowed walls.
37. It Carries Significant Political Symbolism
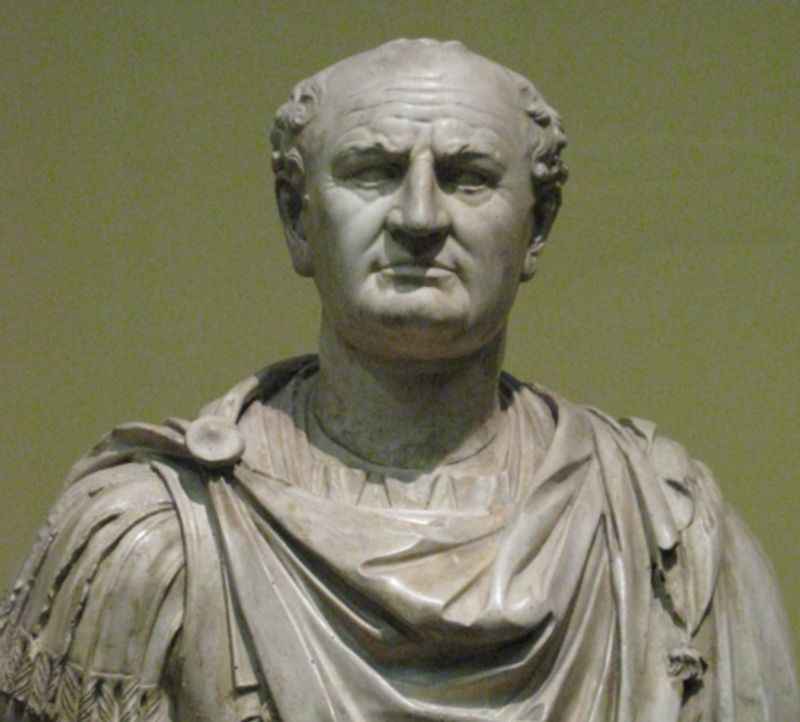

The Colosseum carries profound political symbolism, influenced by the tumultuous period of civil wars in ancient Rome. The building was initiated by Emperor Vespasian and completed under his son Titus, aimed to restore stability and project the image of a united empire.
The Colosseum's grandeur and architectural splendor served as a potent symbol of the Flavian dynasty's power and legitimacy.
The lavish spectacles hosted within its walls were strategically employed to foster a sense of unity and distract the populace from the recent conflicts.
This political symbolism effectively conveyed the message of imperial strength and the restoration of order, solidifying the Colosseum as an enduring symbol of Rome's political might.
38. The Colosseum is a Cultural Icon
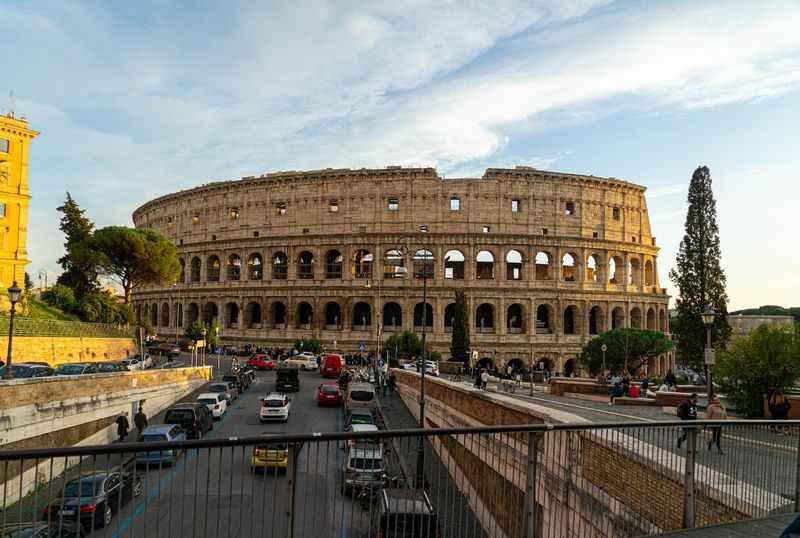

The Colosseum has transcended time to become a cultural icon of immense significance. It represents the grandeur and legacy of ancient Rome, captivating the imagination of people worldwide.
Its architectural magnificence and historical importance make it a cherished symbol of human achievement.
As one of the most recognizable landmarks in the globe, the Colosseum attracts millions of visitors who seek to immerse themselves in its rich heritage. It has inspired countless works of art, literature, and film, becoming a muse for creative expression.
39. It Is Aligned with the Rising and Setting Sun
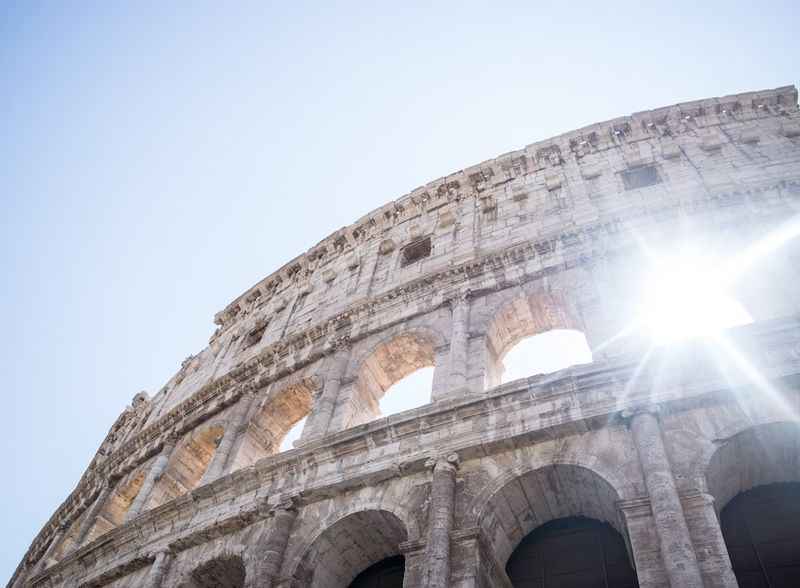

The Colosseum's architectural design exhibits a remarkable alignment with the rising and setting sun, showcasing the ancient Romans' attention to celestial phenomena. The main axis of the Colosseum runs in an east-west direction, allowing the sun to illuminate the arena during specific times of the day.
The morning rays would filter through the eastern entrances, casting a dramatic glow on the gladiatorial battles. In the evening, the setting sun would bathe the western side of the Colosseum in a warm golden light, creating a captivating spectacle.
This intentional alignment not only enhanced the visual experience for spectators but also symbolized the eternal cycle of life and the grandeur of the Roman Empire.
40. The Colosseum Has a Monumental Entrance
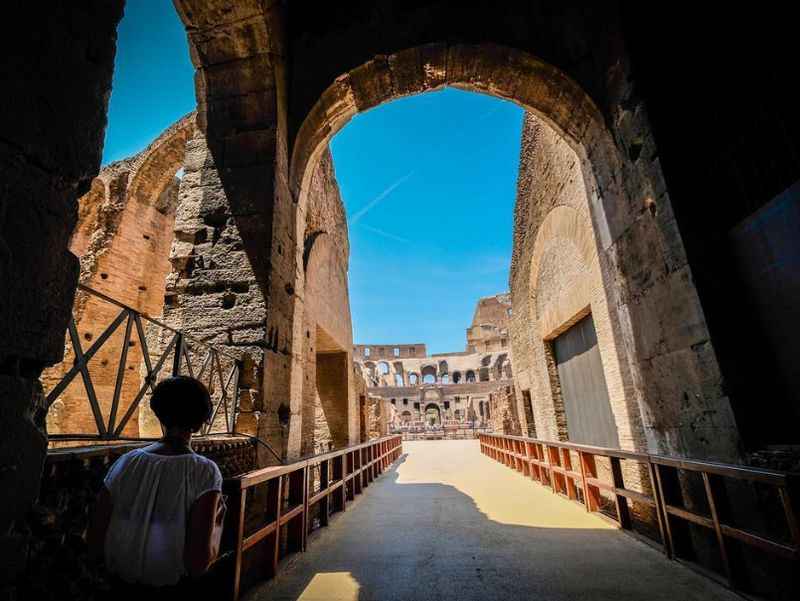

The Colosseum boasts a monumental entrance that commands awe and reverence. Its grandeur is exemplified by the colossal arches and imposing façade that greet visitors. The main entrance, known as the Porta Triumphalis, was reserved for victorious emperors and celebrated generals.
This grand gateway, adorned with ornate sculptures and intricate reliefs, served as a powerful symbol of imperial might and triumph.
Stepping through the monumental entrance, spectators were transported into a realm of gladiatorial contests and larger-than-life spectacles.
The sheer scale and magnificence of the Colosseum's entrance set the stage for the grandeur and splendor that awaited within its iconic walls.
FAQs on 40 Amazing Roman Colosseum Facts
Below are answers to frequently asked questions on 40 amazing Roman Colosseum facts.
Why is the Colosseum of Rome famous?
The Roman Colosseum is famous for being an iconic symbol of the Roman Empire and a popular tourist attraction. It is renowned for its remarkable architecture and historical significance as a famous monument, making it one of the Seven Wonders of the Modern World. The Colosseum arena floor was made of stone, making the gladiatorial games held there gory. With a Rome Tourist Card, you can visit the Colosseum for as much as you want because it has no time limit.
What is interesting about the Roman Colosseum?
The Roman Colosseum is an intriguing structure that was in use for three centuries. It was the largest amphitheater in the Roman world and was previously known as the Flavian Amphitheatre. With eighty entrances, it could accommodate tens of thousands of Romans, serving as a symbol of the powerful Flavian dynasty. Despite being destroyed multiple times by natural disasters, the Colosseum's resilience and enduring legacy continue to captivate visitors from around the world.
What are some dark facts about the Colosseum?
The Colosseum holds dark facts that reveal the brutality of its history. It is alleged that the Colosseum was the site where many early Christians were martyred, and subjected to public executions for their faith. Behind the scenes, the amphitheater housed wild animals that were used for fights and wild animal hunts, adding to the spectacle. Additionally, a somber aspect of its construction is that tens of thousands of Jewish slaves were involved in building this monumental structure, highlighting the harsh reality of forced labor during that era.
Why was the Colosseum built?
The Roman Colosseum was built under the patronage of emperors of the Roman Empire. Its construction served multiple purposes. Firstly, it was a grand showcase of the empire's wealth, power, and engineering prowess. Secondly, the Colosseum was intended to entertain the Roman people, providing a venue for gladiatorial contests, spectacles, and public events that served as a means of distraction and control. Lastly, it was a testament to the desire of the emperors to leave a lasting legacy and assert their authority over the empire.
Summing Up: 40 Amazing Roman Colosseum Facts
The Roman Colosseum is more than just a striking architectural marvel; it is a symbol of the grandeur, entertainment, and brutality that characterized the Roman Empire.
From the blood-soaked gladiator fights to the public executions that occurred within its walls, the Colosseum has witnessed both triumph and tragedy.
Although partially destroyed during World War II, its enduring allure persists, and experiencing this remarkable historical site is one of the most exciting activities Rome.
Today, tourists can grab their Colosseum tickets and step onto the ancient Arena Floor, where legends were born and history was etched.
The Colosseum remains a captivating reminder of the past, inviting visitors to marvel at its awe-inspiring presence and imagine the echoes of its glorious past.













