Reflexive Verbs in Spanish - A Beginner's Guide | 2024 (with Examples)

Mastering reflexive verbs and learning Spanish can be very beneficial for anyone traveling to a Spanish-speaking country.
Spain and Mexico are top Spanish-speaking destinations but there are 20 other countries in which you can put these verbs to good use.
The concept of reflexive verbs in Spanish can be difficult for many beginners to understand. But, believe it or not, reflexive verbs really aren't too difficult to get your head around.
Reflexive verbs are a key part of the Spanish language and you'll need to understand them to communicate effectively.
By the end of this guide, you'll know what a reflexive verb is, what the most common ones are in Spanish, and how to use them in the present tense.
The goal of this post is to answer and provide clarity to the following questions.
1. What are reflexive verbs in Spanish?
2. What is a reflexive pronoun?
3. Where do I place reflexive pronouns?
4. What are the most common Spanish reflexive verbs?
What is a Reflexive Verb?

A reflexive verb in the Spanish language is a verb whose direct object is the same as its subject. In other words, a person is performing an action on oneself.
Whether you're using the present tense, the preterite tense, or any other tense, this rule will always stay the same.
Some examples of reflexive verbs in Spanish ending in -AR are as follows:
- Despertarse - To wake (oneself) up
- Levantarse - To get (oneself) up
- Lavarse - To wash (oneself)
- Ducharse - To shower (oneself)
- Vestirse - To dress (oneself)
Notice anything similar about them? They all have se attached to the end. In Spanish, if a verb is followed by se then it is reflexive.
Reflexive verbs are less common in English, which is what makes understanding them a little difficult sometimes for English speakers.
In English, we use the pronouns 'myself' 'yourself' 'himself' etc. to indicate that a verb is reflexive, but often it is not necessary.
For instance, we say "I shower in the morning", not "I shower myself in the morning". Often, reflexive actions are more implied in English.
In Spanish, using and conjugating a reflexive verb works a little differently.
First, remember that the subject of a sentence is the protagonist of the sentence – whether it’s a person, a place, or a thing.
The object is the person, place, or thing that receives the action performed by the subject.
With reflexive verbs, the subject is doing the action to itself.
Example Sentences
The following examples should make things a little clearer.
- He washes the dishes (not reflexive).
subject: He
verb: washes
object: the dishes
Él lava los platos.
subject: él
verb: lava
object: los platos
- He washes his hands (reflexive).
subject: he
verb: washes
object: his hands (himself: same as the subject)
Él se lava las manos.
subject: él
verb: lava
object: las manos (himself: same as the subject)
Using Reflexive Verbs in Spanish

Reflexive verbs in English are demonstrated with pronouns like myself, himself, ourselves, etc.
In Spanish, this pronoun is already part of the verb. Just look at the 'se' in these reflexive verbs in Spanish below:
- Quitarse - To take off
- Secarse - To dry off
- Mirarse - To look at oneself
In order to conjugate reflexive verbs in Spanish, we need to remove the 'se' from the end of the infinitive form and add the reflexive pronoun to the front of the verb.
Example Sentences
Ella se mira en el espejo - She looks (at herself) in the mirror
subject: ella
verb: mira
object: ella (se: part of the reflexive verb mirarse)
Here, se shows that she is doing the action to herself.
Sometimes, even in English, the object is not always evident. For example:
I get up.
subject: I
verb: get up
object: I (myself)
In English, we do not need to say 'myself' in this context. We already know who is doing the action, since we say 'I'.
In Spanish, however, reflexive verbs make it necessary to demonstrate who is carrying out the action.
Context would be lost completely if you used the Spanish verb conjugation 'levanto' and not 'me levanto.'
Yo me seco - I dry (myself) off
subject: yo
verb: seco
object: yo (me: part of the reflexive secarme)
Remember, the reflexive pronoun should be included in the verb itself.
What is a Reflexive pronoun?

Now, let's explore reflexive pronouns. A reflexive pronoun in English is 'myself', 'yourself', 'himself', 'herself', 'itself', 'ourselves', 'yourselves', and 'themselves'.
Reflexive pronouns in Spanish are used with reflexive verbs when the subject is performing an action to itself.
Example Sentences
Me lavo - I wash (myself)
Nos despertamos - We get (ourselves) up
Os ducháis - You shower (yourselves)
What Are the Reflexive Pronouns in Spanish?
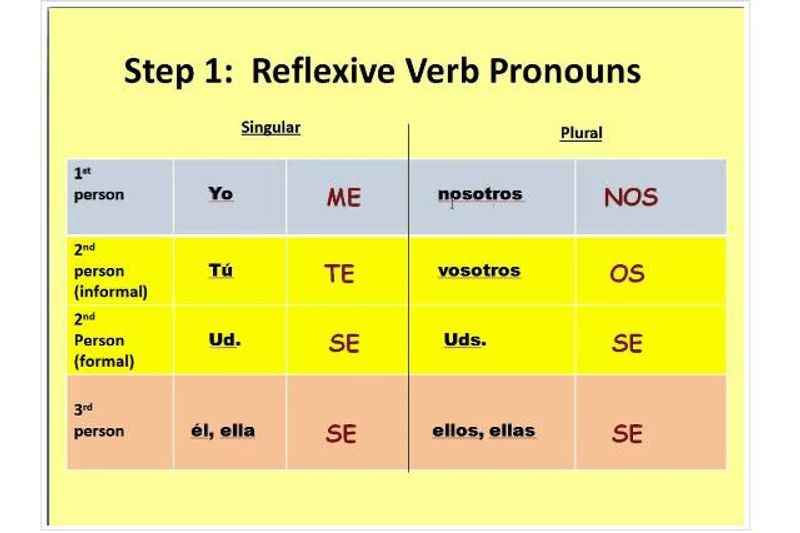
Below you will see the Spanish reflexive pronouns:
- Yo me
- Tú te
- Él/ ella/ usted se
- Nosotros nos
- Vosotros os
- Ellos/ ellas/ ustedes se
How to Conjugate Spanish Reflexive Verbs Using Reflexive Pronouns
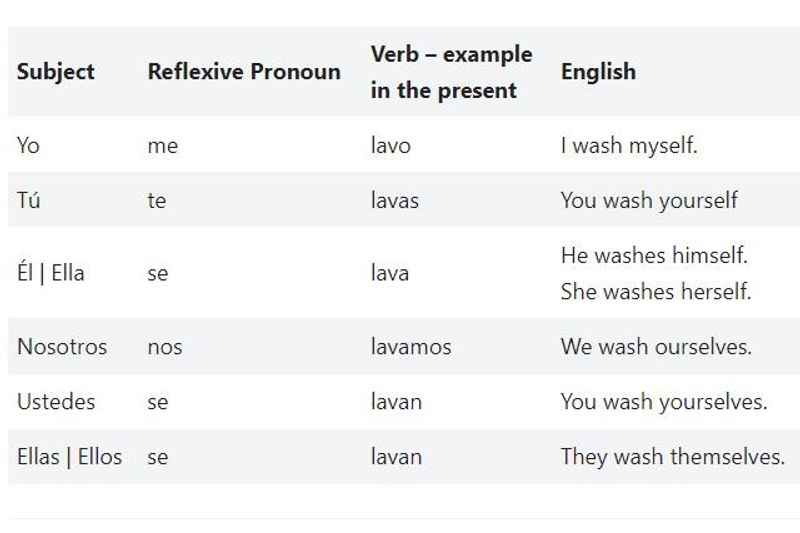
So, now we know what a reflexive verb is and what the corresponding pronouns are, let's take a look at how to conjugate reflexive verbs.
In the table above, you'll see this put into practice. Let's look now at some further examples of Spanish reflexive verbs when conjugated.
Example Sentences
Yo me voy después de comer - I am going out after eating.
Reflexive verb: Irse
Reflexive pronoun: me
Ella se llama Claudia - She is called Claudia.
Reflexive verb: Llamarse
Reflexive pronoun: se
You may have noticed that most reflexive verbs have non-reflexive forms as well, such as ir ("to go") versus irse ("to leave") and llamar ("to call") versus llamarse ("to call oneself"). When you add reflexive pronouns, you make the verb reflexive.
Reflexive Verbs in the Imperative Form

The imperative mood (an order, request, or command) is an important feature of the Spanish language and it is used frequently.
When the verb is in the imperative form then the reflexive pronoun stays at the end of the conjugated form of the verb.
Example Sentences
Bañate antes de que nos vayamos - Take a bath before we go.
Reflexive verb: Bañarse
Lavaos las manos - Wash your hands.
Reflexive verb: Lavarse
Note that the imperative mood gets a little complicated with the vosotros conjugation in the non-reflexive form, but this is a whole separate lesson!
Reflexive Verbs in the Infinitive

If a sentence already has a conjugated verb, you can either put the reflexive pronoun before the conjugated verb OR attach it to the end of the reflexive verb.
Example Sentences
Take the example sentence "Claudia is going to sleep early tomorrow night."
Claudia va a dormirse pronto mañana por la noche.
OR
Claudia se va a dormir pronto mañana por la noche.
In this example, the infinitive ir (to go) is conjugated as va a (is going to) and the reflexive pronoun se can be placed before or after "va a dormir".
The 30 Most Common Reflexive Verbs in Spanish

We've compiled the 30 most common reflexive verbs in Spanish and put them into separate tables, splitting them into AR, ER, and IR verbs.
What you'll see in the tables below is a list of Spanish reflexive verbs in their infinitive form.
As an exercise to improve your Spanish, try to conjugate them in your head, or on paper, using the reflexive pronouns we covered earlier.
What is a Reflexive Verb in a Sentence?

Below are some examples of reflexive verbs in a sentence. You will see the conjugated form in the sentence, with the infinitive version (main verb) in parenthesis.
- Ella se ducha todos los días (duchar_se_)
- Ellos se van después de comer (ir_se_)
- Tú te afeitas tres veces por semana (afeitar_se_)
- Nos lavamos muy a menudo (lavar_se_)
- Ambos se quedan dormidos (quedar_se_)
- No se da cuenta de...(dar_se_ cuenta de)
- Ella se lava demasiado (lavar_se_)
- Ellos se lavan muy poco (lavar_se_)
- La mujer se cansa de ... (cansar_se_ de)
- El chico se fija en ... (fijar_se_ en)
- Nos enamoramos de la ciudad hace mucho tiempo (enamorar_se_ de)
- Nosotros nos afeitamos (afeitar_se_)
Top 5 Verbs in Spanish to Learn (in their reflexive form)

So, what are some of the most important Spanish verbs to learn in their reflexive form?
Well, we have listed a few examples below. Try to learn these with the corresponding reflexive pronoun before you leave this page!
Llamarse - to be called (to call oneself)
In this case, just think about the reply required to the question we all know - "¿Cómo te llamas?"
The reflexive verb llamarse is probably the most common verb you'll come across in early-stage Spanish.
- me llamo
- te llamas
- se llama
- nos llamamos
- os llamais
- se llaman
Afeitarse - (to shave)
- me afeito
- te afeitas
- se afeita
- nos afeitamos
- os afatáis
- se afeitan
Quedarse dormido - (to fall asleep)
- me quedo dormido
- te quedas dormido
- se queda dormido
- nos quedamos dormidos
- os quedáis dormidos
- se quedan dormidos
Levantarse - (to get up)
- me levanto
- te levantas
- se levanta
- nos levantamos
- os levantais
- se levantan
Lavarse los dientes / las manos - (to brush one's teeth / hands)
- me lavo los dientes / las manos
- te lavas los dientes / las manos
- se lava los dientes / las manos
- nos lavamos los dientes / las manos
- os laváis los dientes / las manos
- se lavan los dientes / las manos
FAQs About Reflexive Verbs in Spanish
Now that we have discussed Spanish reflexive verbs we will explore some frequently asked questions relating to this topic.
What are reciprocal reflexive verbs?
Just like the name suggests, reciprocal reflexive verbs are verbs that when used with plural reflexive pronouns, demonstrate that the action is performed by two (or more) subjects at the same time.
How can I learn affirmative commands and negative commands in Spanish?
You can learn the imperative mood (affirmative and negative) from textbooks and grammar guides online. Or, for more fun language practice, listen to songs, watch movies, and engage with social media accounts.
There are many TikTok channels that can help you to learn Spanish and most of them are run by native speakers. Phrases like no te vayas sin suscribirte ("don't leave without subscribing") are common.
Is the Spanish language easy to learn?
Spanish is one of the easier languages you can learn. The language has certain fluency and charm that makes things much easier. Also, it is a widely spoken language across the world so chances are you encountered it many times before which makes learning a bit easier.
Summing Up: Reflexive Verbs in Spanish - A Beginner's Guide
In this article, we have shown you what a reflexive verb is and how you can identify one in a sentence.
Like so many elements in Spanish, such as the imperfect tense, the subjunctive or irregular verbs,
You should now know not only when to use a Spanish reflexive verb, but also how to use one in a sentence, depending on who you want to refer to.
Remember, all you need to change when conjugating in the present tense is the pronoun.
This changes who you are referring to. Good luck and hopefully you will be speaking Spanish while traveling in no time.







